Cross-Peer DNS
Cross-Peer DNS
ℹ️ Information: Cross-Peer DNS allows instances in peered VPCs to resolve DNS hostnames to private IP addresses. This section guides you through enabling and testing Cross-Peer DNS.
💡 Pro Tip: Enabling Cross-Peer DNS can simplify network management by allowing you to use DNS hostnames instead of IP addresses.
Implementation Steps
- Access VPC Management Console
- Select VPCs from the left sidebar
- Select My VPC
- Enable DNS Hostnames
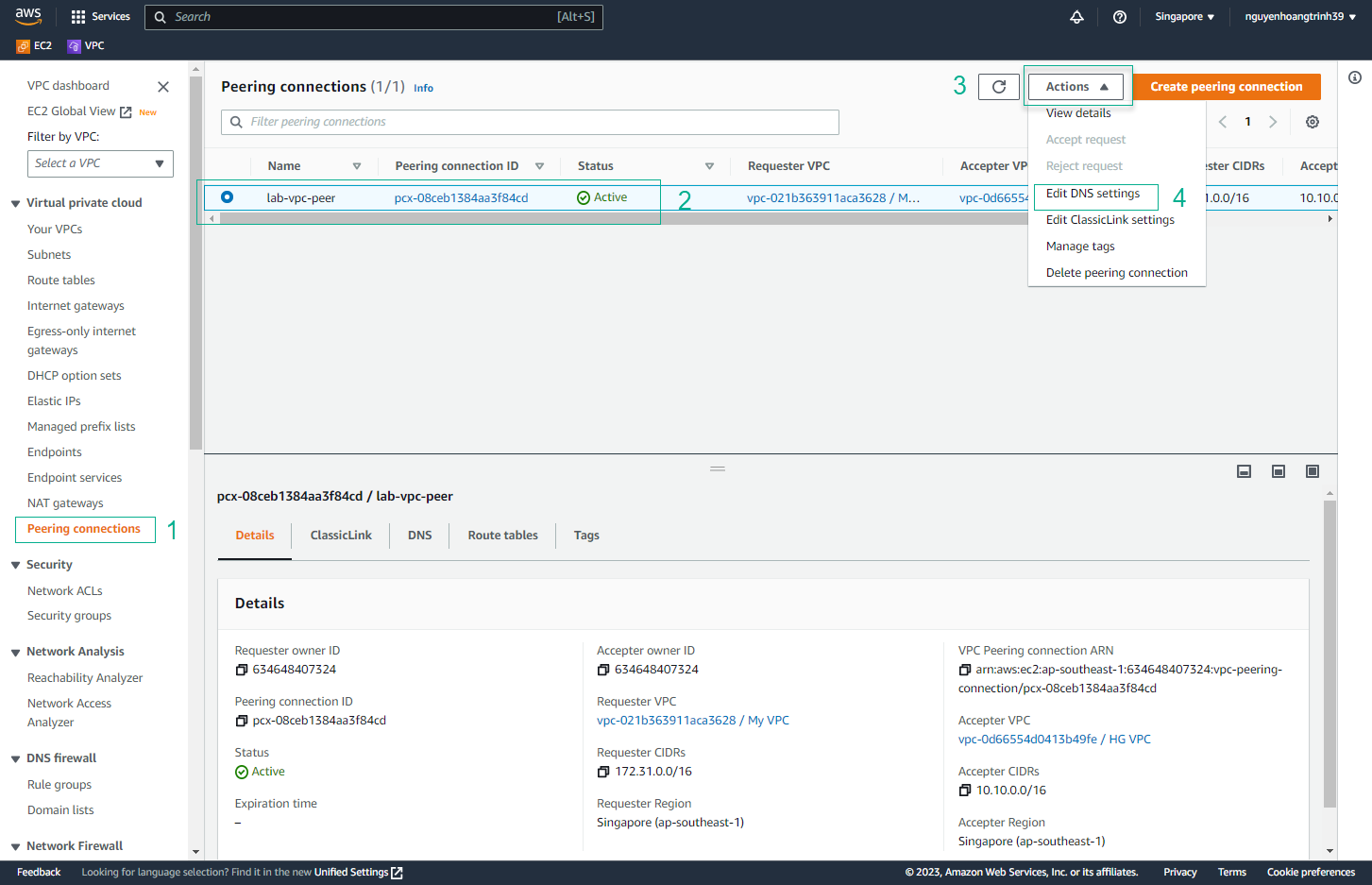
- Click the Actions button
- Select Edit DNS hostnames
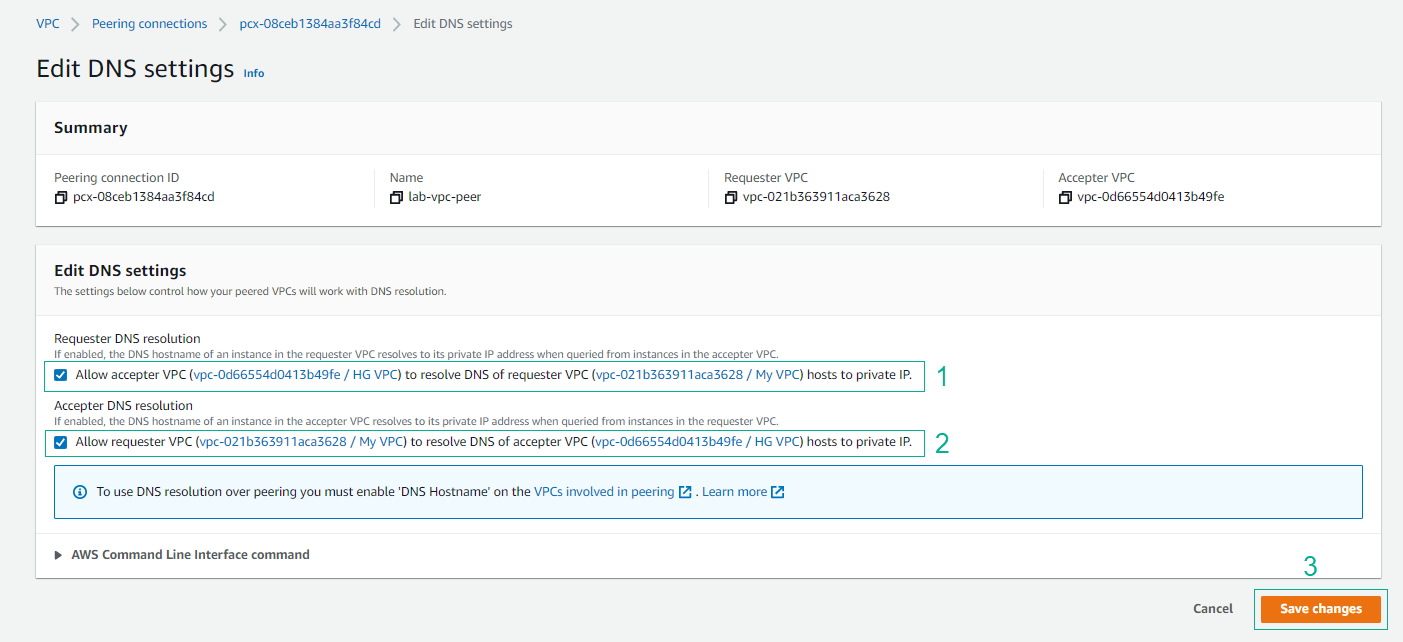
- Enable DNS hostnames
- Click Save
- Repeat for HG VPC
- Select HG VPC
- Enable DNS hostnames
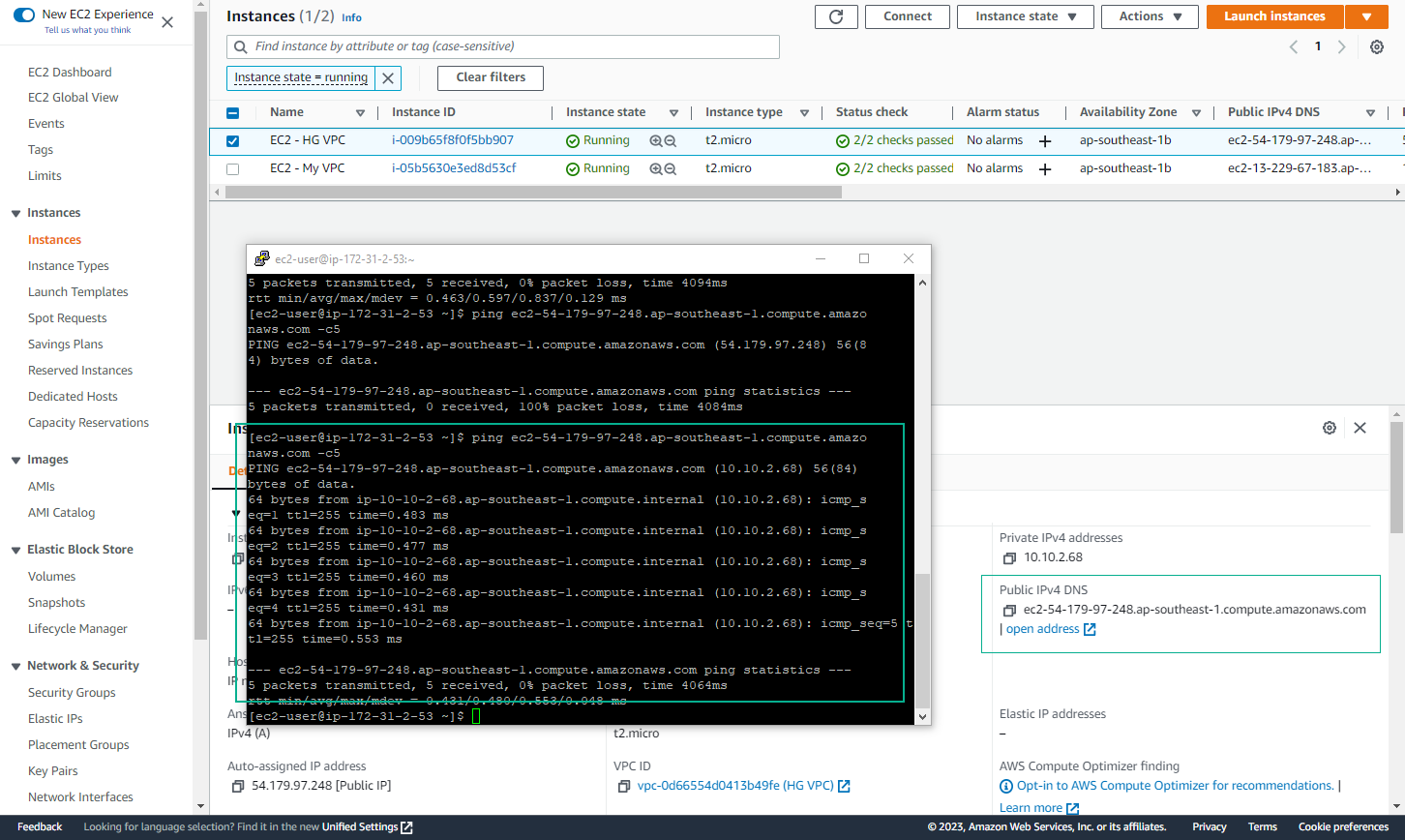
- Test DNS Resolution
- From an EC2 instance in My VPC, use the
nslookupcommand to resolve the DNS hostname of an instance in HG VPC - Verify that the private IP address is returned
- From an EC2 instance in My VPC, use the
- Verify Connectivity
- Use the resolved DNS hostname to ping the instance in HG VPC
- Ensure successful communication
🔒 Security Note: Ensure that your security groups and network ACLs allow DNS traffic (UDP port 53) between the peered VPCs.
⚠️ Warning: DNS resolution must be enabled on both VPCs for Cross-Peer DNS to work. Ensure both VPCs have DNS hostnames enabled.
💡 Pro Tip: Use DNS hostnames instead of IP addresses in your applications to make them more resilient to IP address changes.