Setting up VPC Peering
Overview
ℹ️ Information: By default, VPCs within AWS Cloud are isolated and cannot communicate directly with each other. In this lab, you will establish a VPC Peering connection between two VPCs, enabling direct communication between resources in both VPCs. This eliminates the need for traffic to traverse the public internet, enhancing security and reducing latency.
💡 Pro Tip: VPC Peering is a cost-effective and secure solution for connecting VPCs within the same region or across different regions, even across different AWS accounts.
You will create the following architecture for this lab:
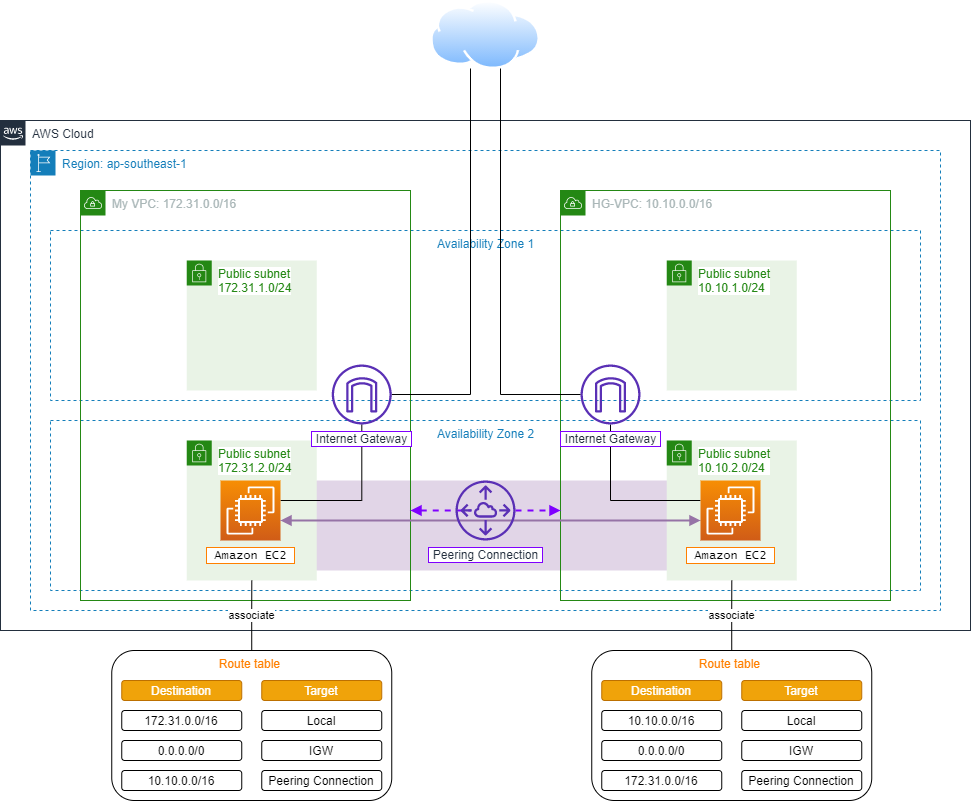
VPC Peering Connection
ℹ️ Information: A VPC Peering connection is a network connection between two VPCs that enables routing of traffic between them using private IPv4 or IPv6 addresses. Instances in either VPC can communicate with each other as if they were on the same network.
🔒 Security Note: VPC Peering does not support transitive peering. If VPC A is peered with VPC B and VPC B is peered with VPC C, VPC A cannot communicate with VPC C through VPC B.
Network Access Control List (Network ACL)
ℹ️ Information: While Security Groups provide stateful firewall protection at the resource level, Network ACLs provide stateless firewall protection at the subnet level. Network ACLs can only be associated with subnets, not individual instances.
💡 Pro Tip: Network ACLs and Security Groups should be used together to implement defense in depth. Network ACLs operate at the subnet level and can block traffic before it reaches Security Groups.
⚠️ Warning: Network ACLs are stateless, meaning you must configure both inbound and outbound rules. Each rule can allow or deny traffic based on port and protocol.
Cross-Peering DNS
ℹ️ Information: Cross-Peering DNS is a VPC Peering feature that enables resources in one VPC to resolve DNS names of resources in another VPC.
💡 Pro Tip: When Cross-Peering DNS is enabled, instances can use DNS names of instances in the peered VPC instead of remembering IP addresses.
⚠️ Warning: Convention: VPC default = VPC 1; HG VPC = VPC 2.
Key Features of VPC Peering
-
Direct Connection:
- No gateway, VPN, or physical connection required
- Traffic traverses AWS backbone network, not the internet
-
Security:
- No shared security perimeter
- Each VPC can manage its own security groups and network ACLs
-
Performance:
- Low latency
- High bandwidth
- No data transfer costs between VPCs
-
Scalability:
- Supports connections between VPCs in the same region
- Supports connections between VPCs in different regions
- Supports connections between VPCs in different AWS accounts